AI in everyday Life (For non-techies)
AI isn't just for experts, it's already in your daily life through voice assistants and spam filters. Learn how these digital tools work, discover tips to use them more effectively, and find out how to set up your own local AI system.

Artificial intelligence has moved from science fiction to an everyday reality that shapes our lives in countless ways. From the moment you wake up to when you go to sleep, AI works quietly in the background, making recommendations, filtering information, and even helping control your home. In this post, I'll explore how AI has evolved, where it shows up in your daily routine, and practical ways to make it work better for you.
But before I begin, what exactly is AI?
At its core, artificial intelligence is technology designed to mimic human thinking. Modern AI systems learn from data to recognize patterns and make predictions. Unlike traditional software that follows fixed instructions, AI can adapt and improve over time, similar to how we learn from experience. This ability to "learn" is what makes AI so powerful in our everyday tools.
Believe it or not, AI has been around since the 1950s! But the AI we know today, the kind that powers your phone's voice assistant or suggests what movie to watch, is relatively new.
In the 1990s, AI hit some growing pains. Early systems relied on rigid rules and struggled with real-world complexity. Think of them like overly strict recipe books that couldn't handle unexpected ingredients. These systems were expensive to maintain and often disappointed.
During this challenging period, AI research continued quietly behind the scenes. Scientists began focusing less on rigid rules and more on teaching computers to learn from examples. By the mid-90s, the field was shifting toward systems that could adapt and improve with experience, laying the groundwork for today's AI revolution.
The real breakthrough came in the last decade when AI finally became part of our everyday lives. In 2011, Apple introduced Siri to the iPhone, and suddenly it felt like our phones could actually understand us. Just a year later, in 2012, researchers created a much-improved learning system that could recognize images with surprising accuracy.
This moment sparked what we now call the AI boom! Almost overnight, technologies that seemed like science fiction became possible: cars that could drive themselves, phones that could understand natural speech, and homes with smart devices that adjust to our habits. These innovations paved the way for the AI tools we now use daily without even thinking about it. From voice assistants that play our favorite songs to streaming services that somehow know exactly what show we'd like to watch next.

AI in 2020's
AI is often the invisible sidekick in everyday gadgets and apps. Let's explore some familiar examples of AI in action in daily life, and how they make things easier or more personal.
Voice Assistants
Voice assistants such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant have become our digital companions. When you say "Hey Siri, tell me a joke" or "Alexa, play some music", AI is listening. It understands your voice and then finds an answer or plays a song for you.
Think of it like talking to a helpful friend who listens, searches for info, and talks back. Behind the scenes, the assistant has learned from thousands of voice examples so it knows what your words mean and what replies make sense. Over time it even adapts to your speech patterns, getting better at understanding your accent or favorite commands.
This means mornings can be smoother, you can set alarms, check weather, or send texts by voice, without lifting a finger.
Smart Home Devices
AI also powers gadgets around our home. For example, a smart thermostat uses AI to learn our comfort preferences (warm in the morning, cooler at night) and adjusts itself, potentially saving energy without us thinking about it.
Recommendation Systems
Have you ever wondered how Netflix knows what shows you might like, or why your Spotify playlist feels just right? That's AI watching your choices. Every time you watch, listen, or shop, AI takes note. It notices patterns such as "this person likes mysteries" or "that person jams to something on Mondays" and then suggests new content it thinks you'll enjoy.
These smart suggestions save you time and help you discover things you might have missed on your own.
Spam Filters
Ever noticed how very few spam emails reach your inbox nowadays? That's AI at work. Email services use intelligent filters to spot unwanted messages (ads, phishing attempts, etc.) and sweep them into spam folders. It's a lot like having a vigilant door guard for your mailbox, who checks every letter and tosses out anything suspicious.
The AI "learner" behind these filters has seen millions of spam examples, so it's extremely good at catching junk. Google says its AI-powered spam filter stops over 99.9% of spam, phishing, and malware from getting to Gmail users.
In practice, that means you get mostly the good mail you care about, which really cuts down on annoyance and risk.

How AI Really Works
Each of these examples might feel complex, but at heart they're powered by AI "learning" from lots of data. Let's break it down in simple terms: AI is like a very trusty sidekick who watches what you do, takes notes, and then tries to help next time.
It learns that you say "play metal" when you wake up, or that you tap heart emojis on workout posts, and adjusts its behavior to match. In everyday use, you can think of AI as your friendly helper who keeps getting smarter the more it learns about you.
Ethics and Practical Concerns
It's awesome having smart helpers, but it's also good to be aware of the trade-offs. Here are a few key concerns to keep in mind, not to scare you though, but so that you're informed.
Privacy & Data Security
AI features usually need data to work well. For example, a personalized news feed needs to know which articles you like, and a voice assistant needs to record your voice commands. All that information can be sensitive. The more data these systems collect (like location, browsing history, health info, etc.), the more we need to trust that it's handled safely. Experts warn that AI's convenience can come with risks like data breaches or misuse of information.
In other words, your personal "profile" is what trains these AI systems for you, so it's wise to check privacy settings: see what data an app really needs and turn off anything extra. Keep your software updated too, since updates often patch security holes. And even more: Who's handling this data? Can this person or organization be trusted?
Algorithmic Bias
Sometimes AI can pick up human prejudices. If an AI system learns from data that's unbalanced (for example, mostly data about one group of people), its suggestions or decisions might end up unfairly favoring or disfavoring some people.
One famous concern is that some facial-recognition software works better on lighter skin tones because its training set was unbalanced. It's like if a teacher graded mostly students of one background better because she was used to teaching them: it's unfair.
Good news is that researchers are aware of this and are working on it, but as users it's good to remember that AI suggestions can reflect quirks in the data they learned from. This is why it's smart to take any AI recommendation with a grain of salt and remember a human check is always important.
Over-reliance
When life gets easier with AI, it's tempting to let it do everything. Relying too much on AI can make us a bit less sharp in some skills. For instance, always following GPS might weaken your own sense of direction, or over-trusting a smart assistant might make us less careful about double-checking information.
It's great to use AI for convenience, but every now and then, it's healthy to double-check things yourself or take a route you know by heart.
Think of AI as a helper, but stay the boss in charge.
Being aware of these concerns lets you enjoy AI's benefits while staying smart about the trade-offs. Remember, like any powerful tool, AI works best when we guide it responsibly.

Tips for Non-Tech Users to Getting the Most from AI
If you're thinking, "This is cool, how do I get more out of AI (and stay safe)?", here I have some friendly tips for you, coming from a tech guy (me).
Customize Your Experience and Train Your AI
Many AI services such as ChatGPT, Claude or Spotify improve if you give feedback. For example, on Netlflix or Spotify, thumb-up your favorite songs or shows so it knows what you like. Over time, your recommendations get more on target.
Similarly, voice assistants let you teach them your pronunciation or favorite commands. Spend a few minutes in the settings of an app: set your preferences (like news topics you care about) or tell the assistant your name and home address. This upfront effort pays off in more useful results.
Protect Your Privacy and Take Control of Your Data
Peek into your app permissions and privacy settings. You might find options to turn off location tracking when it's not needed, or to delete past voice recordings. For instance, you can ofen tell your smart speaker not to store your voice commands permanently.
Use strong, unique passwords for your devices, and enable two-factor authentication if possible. Even better, use a password manager such as 1Password, BitWarden or anything else and never, ever, ever use the same password for different apps or websitesd! Also, regularly update the software you use that often include security fixes, so update your phone and apps when prompted. These small steps help keep your personal info from wandering off.
Be Selective With Personal Data and Choose What You Share
Only link AI services to accounts you really trust. For example, if a fitness app asks permission to access your health records or contacts, decide if that's really needed or just a convenience. Sometimes skipping extra permissions or using alternatives that require less data can be a safer choice.
Learn Basic Commands and Discover Hidden Features
Spend a moment learning what your AI assistant can do. For example, Google Assistant has "Routines" you can set (like saying "good night" to turn off lights and set an alarm). Discovering these features can save you time.
Stay Curious, Ask Questions and Be an Active User
If an AI answer seems weird, feel free to ask "why" or search for a second opinion. AI is smart, but it's not a human's common sense. It can summarize and compute, but it doesn't truly understand context like a friend would. Remember that it has been trained on data which can be biased or anything.
If something sounds off, verify. This keeps you in control and helps "train" your own knowledge.
Basically, treat AI tools as partners. Tweak their settings to your liking, give them good data (like rating content), and keep an eye on what information you share. Use them to enhance your routine, but don't feel locked in. You can always turn off a feature or switch services if it doesn't feel right.

Using AI Tools in Everyday Life
When we talk about "AI" today, we often mean friendly chatbots and smart assistants that can help us with daily tasks. Popular examples include ChatGPT (by OpenAI) and Claude (by Anthropic). These are cloud-based AIs, you use them over the internet. They are free to try (usually with basic features) and very convenient.
Cloud AI tools have big advantages: they run on company servers, so you don’t need a fancy computer and they’re always updated with the newest models. For example, using ChatGPT or Claude is as simple as opening a browser or smartphone app and chatting.
However, there are trade-offs. All of the text you type is sent over the internet to their servers. That means your data travels out of your computer, which raises privacy concerns. Also, the most advanced features or larger models (like GPT-4o on ChatGPT) require a paid subscription. In short, cloud AI is very convenient, but less private and sometimes costs money for premium power.
On the other hand, you can run AI locally on your own computer or device. This means downloading a program and using models that live right on your machine, without ever sending your data online. There are now user-friendly tools like LM Studio and Ollama for this. These let you "easily run LLMs like LLaMA or DeepSeek on your computer" with no expertise required.
The big benefit here is privacy and control: everything stays on your device, and you don’t pay per query.
Recommended AI Tools to Try
Here are some specific tools to check out, ranging from easy cloud apps to offline models:
- ChatGPT (OpenAI): A very popular chatbot you can use on openai.com or via the mobile app. It has a free tier (GPT-3.5) and a paid "Plus" plan for GPT-4. It's great for writing assistance, answering questions, tutoring help, and more.
- Claude (Anthropic): Another conversational AI you can try at claude.ai. It's built to be "helpful, honest, and harmless," and excels at tasks like summarization, creative writing, and Q&A. For example, Claude can assist with summarizing articles or drafting ideas, often with a very natural style. Quora even offers Claude within their Poe app (so you can chat with multiple AIs in one place).
- Poe (Quora): An all-in-one AI chat app (on web and mobile) that connects you to several bots, including ChatGPT, Claude, and others. Poe makes it easy to switch between different AI assistants without leaving the app. There's a free version and optional paid features.
- Perplexity AI: A search/chat tool that uses AI to answer questions with citations. It's free with pro options, and it's handy for research or fact-based queries. For example, you can ask Perplexity to gather quick facts or compare options when making a decision.
- Open-source models (LLaMA, Mistral, etc.): These are free-to-use AI models created by research groups (Meta's LLaMA models, and Mistral AI's releases, among others). They aren't "apps" by themselves but are often available through local tools (such as LM Studio).
- LM Studio (Windows, Mac): An app for downloading and chatting with open-source LLMs offline. It lets you pick models like LLaMA, DeepSeek, or Mistral and run them on your PC. The website even says you can do it "with no expertise required". (Good for someone who wants local AI without complex setup.)
- Ollama (macOS/Linux/Windows): Another local LLM platform. It provides a simple command-line or app interface to run models like Llama 3, Mistral, and Gemma on your machine. Ollama focuses on privacy (since it's local) and ease of use for developers.
Both LM Studio and Ollama make offline AI much more accessible. You can try them if you're curious about "AI without the internet," but for most everyday users, starting with cloud services is easiest.
How a Good Prompt Works
Think of prompting as having a conversation with a very smart, but sometimes literal friend. The way you ask questions makes all the difference in getting helpful answers! Here's how to get the most from AI assistants:
The Anatomy of an Effective Prompt
A good prompt has a few key ingredients that help the AI understand exactly what you want:
- Be specific and clear: Instead of asking "Tell me about dogs," try "Explain the health benefits of walking a dog daily for a middle-aged person". The more specific you are, the more tailored the response will be.
- Provide context: Let the AI know why you're asking or how you'll use the information. For example: "I'm planning a 3-day trip to Seattle with young children. What are some family-friendly activities there?"
- Specify format when needed: If you want a list, table, or particular structure, just ask! For example: "Create a 7-day meal plan for a vegetarian with high protein needs. Format it as a day-by-day breakdown with each meal listed separately".
- Use examples: Sometimes showing is better than telling. If you want a certain writing style or approach, include a short example: "Write a product description for my handmade candles in the same friendly tone as this: 'Our cozy blankets wrap you in cloud-like comfort, perfect for those quiet Sunday mornings with a book and tea.'"
Prompt Patterns That Work
Here are some tried-and-true prompt patterns that consistently deliver good results:
- The role prompt: "Act as a [role] and help me with [task]". For example: "Act as a fitness coach and create a beginner-friendly 30-minute home workout".
- The step-by-step request: "Explain how to [do something] in simple steps". For instance: "Explain how to troubleshoot a slow computer in simple steps".
- The comparison prompt: "Compare [X] and [Y] in terms of [aspects]". Such as: "Compare meal kit delivery services and grocery shopping in terms of cost, convenience, and environmental impact".
- The refinement prompt: After getting an initial response, you can say "That's great, but can you make it more [characteristic]?". Like: "That's helpful, but can you make it more casual and add some humor?" (The trick here is encouraging the AI)
Common Prompt Mistakes to Avoid
Even smart AI can get confused. Here are pitfalls to avoid:
- Being too vague: "Write something good" doesn't give the AI enough direction.
- Contradictory instructions: Asking for "a comprehensive guide that's also very brief" sends mixed signals.
- Forgetting to specify audience: The explanation suitable for a 5-year-old is very different from one for a college student.
- Information overload: Including tons of unnecessary details can distract the AI from your main question.
Remember, prompting is a skill that improves with practice. Don't hesitate to refine your prompt if the first response isn't quite what you wanted. Often the best approach is to start a conversation and iterate, just like you would when explaining a task to a human assistant!
AI Use Cases in Daily Life
AI chatbots can help with tons of everyday tasks. Here are some categories and examples:
Productivity
AI can tackle routine chores so you can focus on what matters. For instance:
- Email Drafting: Stuck on how to word an email? Tell ChatGPT the main points and it can craft a clear, polite message or improve your draft.
- To-Do Lists: Ask an AI to help organize your day. It can turn a bulleted shopping list or notes into a well-structured to-do list.
- Summarizing Long Texts: Paste a long article, report, or set of notes, and ChatGPT or Claude can give you a concise summary.
- Scheduling Help: Need a meeting agenda or reminders? You can ask your AI to propose a schedule or generate reminders (though you'd still add them to your calendar manually).
These tools save time. The result? Many users report completing writing and planning tasks faster and better than before.
Learning
AI can be like a personal tutor or explainer. Try things like:
- Study Help: Ask the bot to explain a concept simply (e.g. "Explain photosynthesis to me like I'm 12 years old"). It can break down topics step-by-step, provide analogies, or quiz you with practice questions.
- Language Learning: Practice a new language by having conversations or translating phrases. The AI can correct your sentences or help build vocabulary.
- Tutoring/Explanations: If you're curious about something or need a quick lesson, chat with it. For example, ChatGPT or Claude can guide you through basic math, science topics, or even give a "crash course" on personal finance or other subjects.
- Homework Brainstorming: If you're stuck on ideas (say for a school project or learning how to code), the AI can suggest approaches or resources.
Think of AI as a patient study buddy: it won't judge wrong answers, and you can ask it to clarify or repeat things in different words until you understand.
Creativity
AI can kickstart your creative projects. For example:
- Writing Inspiration: Need ideas for a blog post, story, or social media caption? You can brainstorm with ChatGPT or Claude. Give it a topic or title, and ask for an outline or catchy hooks.
- Content Writing: Once you have an outline, AI can help draft paragraphs. It can also check your writing style (e.g. make it friendlier or more professional).
- Image Prompts: If you use AI art tools (like DALL·E or Midjourney), you can ask ChatGPT to generate a detailed text prompt for the image you want.
- Jingles & Poems: For fun, you can have the AI compose a quick poem, song lyrics, or even a short story.
- Editing: AI can proofread and suggest edits to your writing. It catches grammar mistakes or awkward phrasing.
These creative use cases work especially well with cloud AIs. You can ask things like "help me write a friendly travel blog introduction" or "give me 10 blog post ideas about gardening," and get instant suggestions.
Budgeting & Personal Finance
AI can make money management easier:
- Spending Summaries: You might not give an AI access to your bank, but you can manually share spending totals. For example, tell ChatGPT your expenses and income, and it can help you categorize them or suggest a budget.
- Savings Tips: Ask AI for general advice. It can explain budgeting categories, debt-payoff strategies, and more.
- Budgeting Apps: There are AI-powered apps like Cleo (a chatbot) or Rocket Money that hook into your accounts. They automatically analyze where your money goes and can even humorously alert you if you overspend. These apps do the number-crunching for you.
- Planning Purchases: You can also use a bot to plan for big purchases. For instance, ask it to compare prices in different stores or to plan a grocery list that fits your budget.
- Simple Tracking: If you prefer not to link accounts, just jot down a list of expenses and let an AI make sense of it. It can summarize totals and trends, and suggest if you're spending too much on one category.
In short, AI tools can handle the grunt work of math and lists, so you can focus on the big decisions. The AI won't replace a human financial advisor, but for everyday budget planning and tips, it's a handy assistant.
Health & Lifestyle
AI can also help with personal well-being routines:
- Meal Planning: Tell ChatGPT your dietary preferences (e.g. "I'm vegetarian and want high-protein meals"), and it can suggest a week's worth of recipes and shopping list. Always double-check for allergies or medical issues, but it's great for inspiration.
- Habit Tracking: Describe habits you want to build (like daily exercise or reading) and ask for tips to stick with them. The AI can suggest a plan or tools, such as apps or printable trackers.
- Workout Suggestions: You can get basic workout plans (e.g. "30-minute home workout for beginners with no equipment"). The AI will give sample exercises or routines.
- General Advice: Ask for quick tips on sleep, stress relief, or time management. The answers won't be tailored medical advice, but can be helpful reminders (like "drink more water" or "try a short walk").
Remember, the AI offers ideas and motivation, but don't skip consulting professionals for medical or serious health issues.
Get started
Now that we know about where we can use AI in our lives, let's see what our options are for using them.
Free vs. Paid Options
Most of these tools have free tiers. For instance, ChatGPT and Perplexity let you try basic features for free. Poe is free to use multiple bots. Claude offers a free plan with limits. However, advanced features often cost extra. ChatGPT's top model (GPT-4) and Claude's highest version are behind a paywall (usually around $20/month for ChatGPT Plus).
Paid plans can be worth it if you use AI a lot or need the best results. Local tools like LM Studio and Ollama are generally free to install and use (though you might buy a faster GPU to run big models).
In choosing free vs. paid, consider how much you rely on AI. If you only ask quick questions once in a while, the free versions are great. If you're a heavy user (e.g. doing research, long documents, or business tasks), a paid upgrade can save time and give better answers. And if privacy is a top concern, using local free models might be the best "cost" answer.
Installing LMStudio
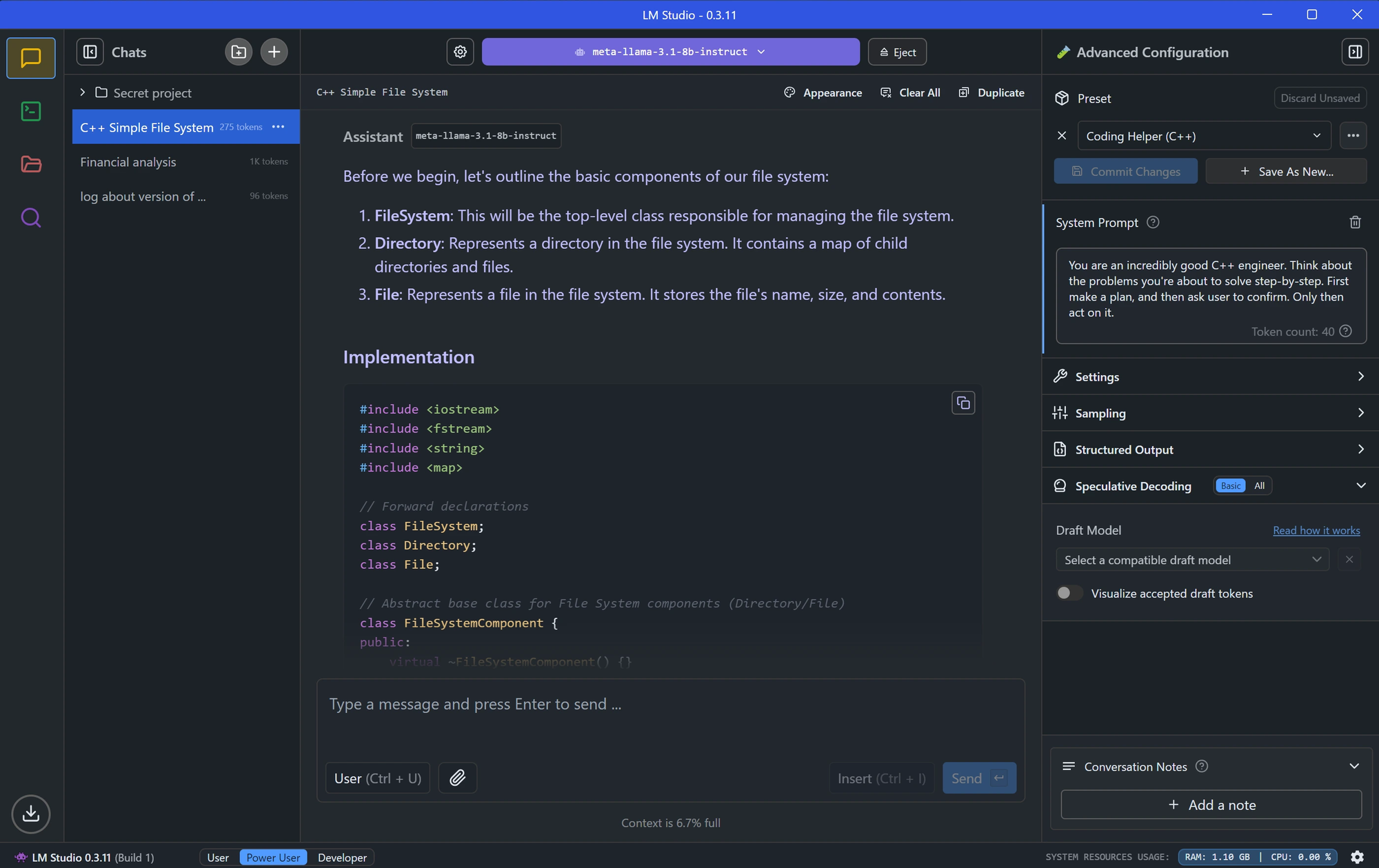
Installing LMStudio is as easy as visiting their website and installing the app on you operating system.
After that, you may want to open the models (by clicking on the purple magnifying glass icon). Then search for open source models that are also compatible on your system. Which will usually recognizable from this notification:

I personally recommend installing "DeepSeek R1 Distill (Qwen 7B)" which is compatible on most devices we have in our homes.
Also make sure that you set the UI to "User" to make it simpler for yourself.
Getting Started Tips
- Just Ask! The hardest part is often thinking of a question. Start with simple tasks: "Help me draft a friendly birthday email," or "Explain how photosynthesis works in simple terms." Use conversational language as if you were talking to a knowledgeable friend.
- Be Specific: Give the AI context so it can tailor answers. E.g., "I have 30 minutes. What exercises can I do at home?" versus "Give me exercises."
- Use Web or Apps: Non-tech users should start with websites or mobile apps. Go to chat.openai.com for ChatGPT, claude.ai for Claude, or download the ChatGPT/Claude app on your phone. Poe and Perplexity have easy websites too. No installation needed for cloud services.
- Try Both Cloud and Local (if curious): If you want more privacy, try a local AI app. LM Studio is user-friendly: install it, pick a model, and chat without an internet connection. Ollama works similarly on Mac or PC. There's usually documentation to walk you through the first run.
- Learn as You Go: Don't worry about using "smart" prompts. Start with everyday language. Watch some tutorial videos or read quick how-tos if needed (there are many beginner guides online). The AI often corrects or asks follow-up questions if it needs more info.
Remember, these AI tools are designed for everyone, not just tech experts. You don't need to know coding or machine learning. Just talk or type, and you'll see how they can become helpful parts of your daily routine!

Comments